Enhance Your Project Management Mojo in 2024: 16 Skills That Speak Volumes!
-
 Rohan Dua
Rohan Dua
- Feb 16, 2024
-
 Tech Career
Tech Career
- 03 Mins read

Understanding the Project Manager Role
In the dynamic landscape of project management, the role of a Project Manager is multifaceted, demanding a diverse skill set to navigate challenges and drive success. A project manager serves as the linchpin, overseeing tasks from initiation to completion. Let's delve into the intricacies of this crucial role.
Key Responsibilities of a Project Manager:
- Initiation and Planning: Define project scope, objectives, and stakeholders. Develop a comprehensive project plan.
- Execution: Coordinate resources and tasks for project implementation. Ensure adherence to timelines and quality standards.
- Monitoring and Controlling: Track project progress and make real-time adjustments. Implement effective quality control measures.
- Closing: Evaluate project outcomes against initial goals. Document lessons learned for future improvements.
Essential Skills for Project Managers
Mastering the art of project management requires a diverse skill set. Project managers should possess a combination of technical expertise, interpersonal skills, and strategic thinking. Let's explore these skills in detail.
1. Knowledge of Product Development Lifecycle:
Understanding the phases of product development is fundamental for effective planning and execution.
2. Market, Industry, and Competition Understanding:
Staying informed about market trends, industry dynamics, and competitive landscapes informs strategic decision-making.
3. Strong Project Management Skills:
Efficiently managing projects to meet deadlines and objectives is foundational.
4. Balancing Short-term and Long-term Goals:
Striking a balance between immediate project needs and long-term strategic objectives is crucial for sustained success.
5. Strategic Thinking and Problem-solving Abilities:
The ability to think strategically and solve complex problems is vital for overcoming challenges.
6. Effective Communication and Leadership Skills:
Strong communication and leadership facilitate collaboration across diverse teams.
7. Product Road Mapping and Backlog Management Experience:
Structuring product development through road mapping and backlog management is crucial for seamless execution.
8. Technology Understanding:
Grasping technology's application to products aligns business goals with technological capabilities.
9. Cross-functional Collaboration:
Seamless collaboration with design, engineering, sales, and marketing teams is essential for holistic project management.
10. Analytical and Data-driven Decision-making Skills:
Strong analytical skills and data-driven decision-making are vital for informed choices.
11. Presentation and Storytelling Skills:
Clear presentation and storytelling convey ideas persuasively, gaining stakeholder buy-in.
12. Familiarity with Agile Methodologies and Tools:
Experience with agile methodologies and tools like Jira, Trello, and Asana streamlines product management processes.
13. Driving Product Development from Ideation to Launch:
Proactively leading product development ensures continuous improvement and innovation.
14. User-centered Design Knowledge:
Understanding user-centered design principles enhances user satisfaction, a critical aspect of product success.
15. Negotiation and Influencing Skills:
Strong negotiation and influencing skills are vital for effective stakeholder management.
16. Understanding of Product Pricing and Revenue Models:
Familiarity with pricing and revenue models is crucial for financial success and profitability.
PMP Certification - Elevating Your Project Management Career
The Project Management Professional (PMP) certification is a hallmark of excellence in project management. Attaining this certification can significantly propel your career forward. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to obtain your PMP certification.
1. Meet Certification Requirements:
Accumulate 35 hours of project management course training and 36 months of project management experience (with a four-year degree) or 35 hours of training with 60 months of experience (with an associate degree or high school diploma).
2. Application Process:
Create an account with the Project Management Institute (PMI), submit your application, and provide details about your educational background and project work.
3. Exam Preparation:
Engage in rigorous exam preparation, either through coursework or self-study, dedicating 60 to 120 hours for effective preparation.
4. Take the PMP Exam:
Schedule and take the PMP exam, which can be conducted at a testing site or online, lasting approximately four hours.
5. Maintain Certification:
The PMP certification is valid for three years. Spend 60 hours on professional development activities within this period to maintain certification.
Is PMP Worth It?
The PMP certification offers various professional and financial benefits, making it a worthwhile investment for aspiring and seasoned project managers.
1. Industry Recognition:
Demonstrates in-depth project management knowledge, enhancing professional credibility.
2. Skill Enhancement:
The certification process imparts valuable project management skills, contributing to career growth and success.
3. Higher Salaries:
PMP-certified professionals often command higher salaries, with median figures showcasing financial benefits.
4. Job Prospects:
The demand for project management professionals is projected to rise across various sectors, presenting abundant job opportunities.
Bonus Tip - The Management Matrix
Effective management is integral to successful project outcomes. Utilize the management matrix to tailor your approach based on employee skills and internal drive.
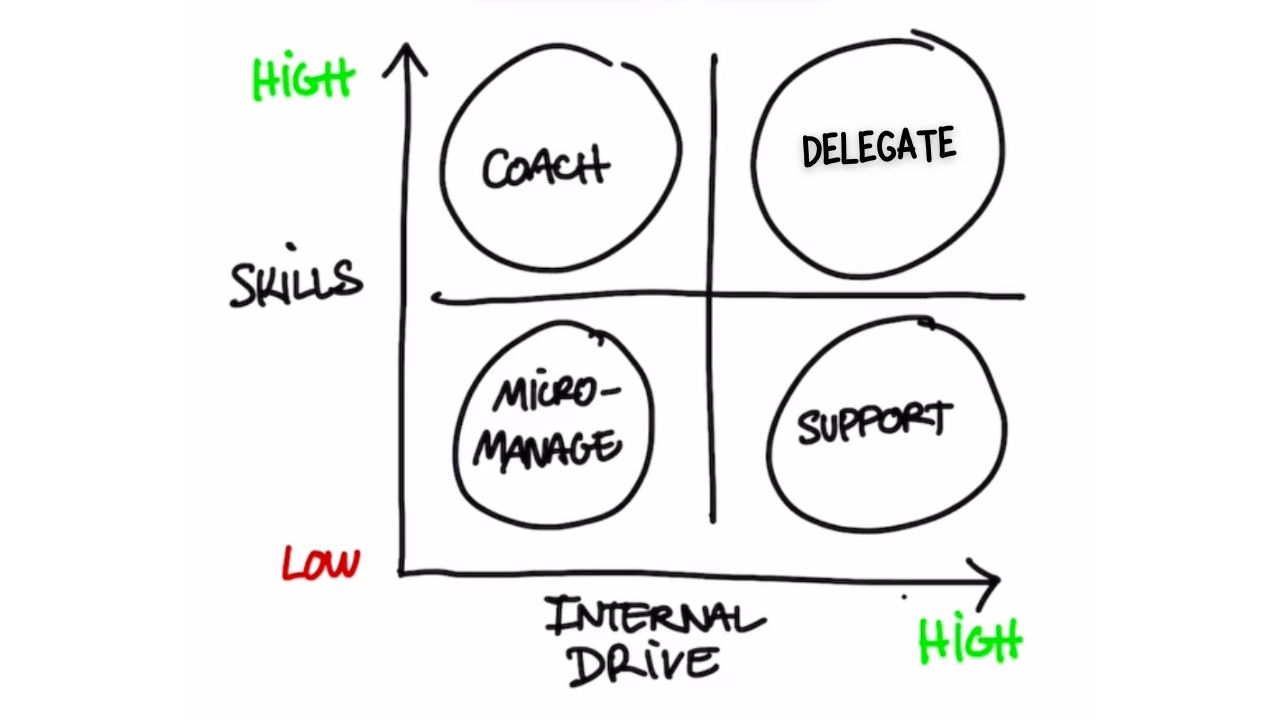
1. Low Skills, Low Internal Drive: Micromanage
Provide detailed guidance and closely supervise tasks to ensure accuracy and alignment with objectives.
2. High Skills, High Internal Drive: Coach
Encourage autonomy, provide guidance when needed, and focus on skill enhancement through continuous learning.
3. High Internal Drive, Low Skills: Support
Offer support, training, and resources to enhance skills and foster growth, promoting a supportive work environment.
4. High Skills, High Internal Drive: Delegate
Delegate responsibilities, empower decision-making, and encourage innovation to harness the full potential of skilled and motivated individuals.
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide equips aspiring and seasoned project managers with the knowledge, skills, and strategies needed to excel in the dynamic field of project management. Whether navigating the intricacies of project execution or pursuing PMP certification, this guide serves as a valuable resource for career growth and success.


